- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
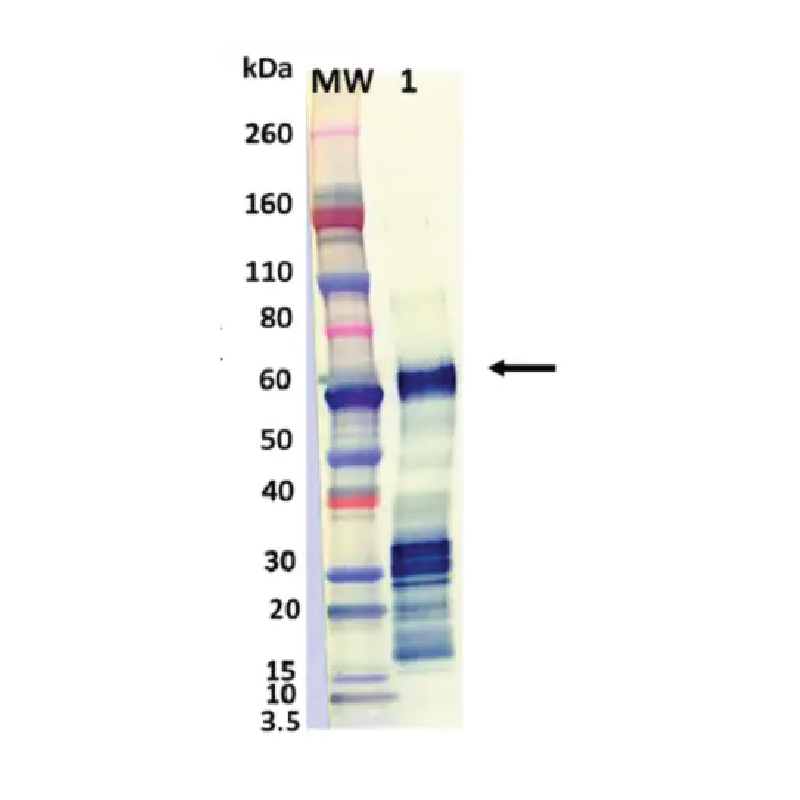
Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay Kit
Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay Kit
This product is currently out of stock and unavailable.
Key features and details
- Assay type: Quantitative
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Assay time: 2 hr
- Sample type: Cell culture media, Cell Lysate, Other biological fluids, Plasma, Serum, Tissue Extracts, Urine
Overview
Product name
Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay KitDetection method
ColorimetricSample type
Urine, Serum, Plasma, Other biological fluids, Tissue Extracts, Cell Lysate, Cell culture mediaAssay type
QuantitativeAssay time
2h 00mProduct overview
Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay Kit ab65329 can measure either the combination of both small molecule antioxidants and proteins, or small molecules alone in the presence of our proprietary Protein Mask.
In the total antioxidant capacity assay protocol, the Cu2+ ion is converted to Cu+ by both small molecule and protein antioxidants. The Protein Mask prevents Cu2+ reduction by proteins, enabling the analysis of only the small molecule antioxidants. The reduced Cu+ ion is chelated with a colorimetric probe giving a broad absorbance peak around 570 nm, proportional to the total antioxidant capacity.
Total antioxidant capacity assay protocol summary:
– add protein mask to samples if only measuring small molecule total antioxidant capacity
– add samples and standards to wells
– add Cu2+ solution and incubate for 90 min at room temp
– analyze with microplate readerNotes
This product is manufactured by BioVision, an Abcam company and was previously called K274 Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) Colorimetric Assay Kit. K274-100 is the same size as the 100 test size of ab65329.
Antioxidants play an important role in preventing the formation of, and scavenging of, free radicals and other oxidizing species. There are three categories of antioxidant species: enzyme systems (GSH reductase, catalase, peroxidase, etc.), small molecules (ascorbate, uric acid, GSH, vitamin E, etc.) and proteins (albumin, transferrin, etc.).
Trolox is used to standardize antioxidants, with all other antioxidants being measured in Trolox equivalents. Measurement of the combined non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity of biological fluids and other samples provides an indication of the overall capability to counteract reactive oxygen species (ROS), resist oxidative damage and combat oxidative stress-related diseases.
Related products
Review the oxidative stress marker and assay guide to learn about more assays for oxidative stress.
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
Storage instructions
Store at +4°C. Please refer to protocols.Components Identifier 100 tests Assay Diluent WM 1 x 10ml Cu++ Reagent Blue 1 x 0.2ml Protein Mask NM 1 x 10ml Trolox Standard (1 µmol) (Lyophilized) Yellow 1 vial Research areas
- Kits/ Lysates/ Other
- Kits
- Cell Damage Kits
- Oxidative stress
- Kits/ Lysates/ Other
- Kits
- Cell Damage Kits
- Cell Damage
- Kits/ Lysates/ Other
- Kits
- Cell Metabolism Kits
- Oxidative Stress Assay Kits
- Oxidative Stress
- Kits/ Lysates/ Other
- Kits
- Cell Damage Kits
- Antioxidant
Relevance
Antioxidants play an important role in preventing the formation of and scavenging of free radicals and other potentially toxic oxidizing species. There are three categories of antioxidant species: enzyme systems (GSH reductase, catalase, peroxidase, etc.), small molecules (ascorbate, uric acid, GSH, vitamin E, etc.) and proteins (albumin, transferrin, etc.). Different antioxidants vary in their reducing power, and cooperation of all different antioxidants provides greater protection against reactive oxigen or nitrogen radicals than any single compound alone. Therefore, the overall total antioxidant capacity may give more relevant biological information compared to that obtained by the measurement of individual components, as it considers the cumulative effect of all antioxidants present.