- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
Pig IL-1 beta ELISA Kit
Pig IL-1 beta ELISA Kit
This product is currently out of stock and unavailable.
Key features and details
- Sensitivity: 6 pg/ml
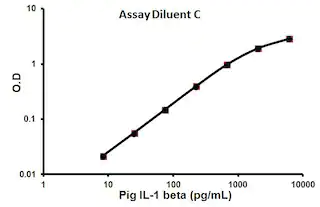
- Range: 8.23 pg/ml – 6000 pg/ml
- Sample type: Cell culture supernatant, Plasma, Serum
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Assay type: Sandwich (quantitative)
- Reacts with: Pig
Overview
Product name
See all IL-1 beta kits
Detection method
Sample type
Assay type
Sensitivity
Range
Recovery
90 %
| Sample type | Average % | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Cell culture supernatant | 96.91 | 89% – 104% |
| Serum | 97.32 | 88% – 105% |
| Plasma | 87.75 | 80% – 92% |
Assay duration
Species reactivity
Product overview
Abcam’s IL1 beta Pig ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of pig IL1 beta in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants.
This assay employs an antibody specific for IL1 beta coated on a 96-well plate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and IL1 beta present in a sample is bound to the wells by the immobilized antibody. The wells are washed and biotinylated anti-pig IL1 beta antibody is added. After washing away unbound biotinylated antibody, HRP-conjugated streptavidin is pipetted to the wells. The wells are again washed, a TMB substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of IL1 beta bound. The Stop Solution changes the color from blue to yellow, and the intensity of the color is measured at 450 nm.
Platform
Properties
Storage instructions
| Components | 1 x 96 tests |
|---|---|
| 20X Wash Buffer | 1 x 25ml |
| 5X Assay Diluent B | 1 x 15ml |
| 600X HRP-Streptavidin Concentrate | 1 x 200µl |
| Assay Diluent C | 1 x 30ml |
| Biotinylated anti-Pig IL-1 beta | 2 vials |
| IL1 beta Microplate (12 x 8 wells) | 1 unit |
| Recombinant Pig IL-1 beta Standard (lyophilized) | 2 vials |
| Stop Solution | 1 x 8ml |
| TMB One-Step Substrate Reagent | 1 x 12ml |
Research areas
- Immunology
- Innate Immunity
- Cytokines
- Interleukins
- Microbiology
- Organism
- Virus
- RNA Virus
- ssRNA positive strand virus
- SARS Coronavirus
- Cancer
- Tumor immunology
- Cytokines
- Interleukins
- Cardiovascular
- Atherosclerosis
- Vascular Inflammation
- Inflammatory mediators
- Kits/ Lysates/ Other
- Kits
- ELISA Kits
- ELISA Kits
- Cytokines and cytokine receptors ELISA kits
- Metabolism
- Types of disease
- Obesity
- Neuroscience
- Processes